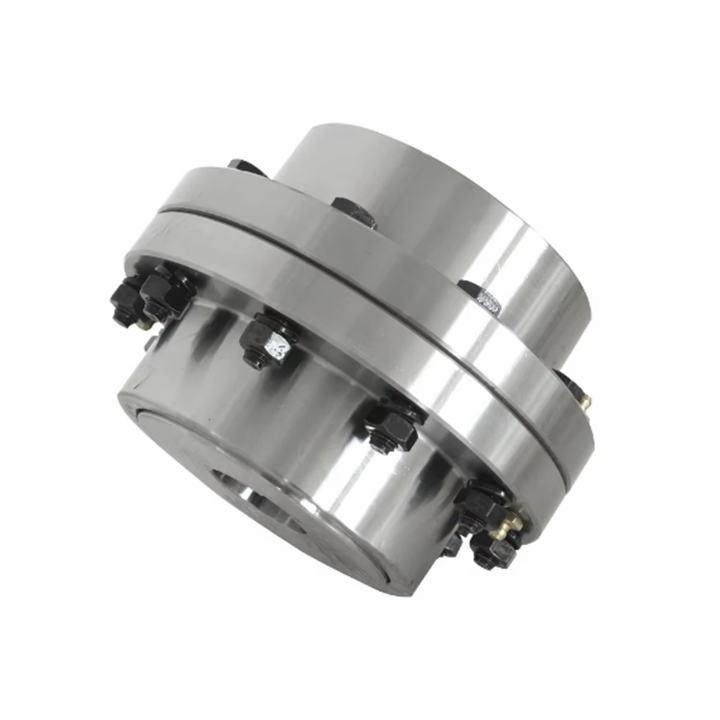
What Is a Coupling?
A Coupling is a mechanical component used to connect two rotating shafts in order to transmit power, torque, or motion from one part of a system to another. Couplings are widely used in industrial machinery, manufacturing equipment, and power transmission systems where reliable and stable operation is required.
In modern mechanical systems, a Coupling does more than simply join shafts. It also helps accommodate misalignment, reduce vibration, and protect connected equipment from excessive mechanical stress. Because of these critical functions, consistent production quality and standardized manufacturing processes are essential, especially when Couplings are supplied in bulk for industrial use.
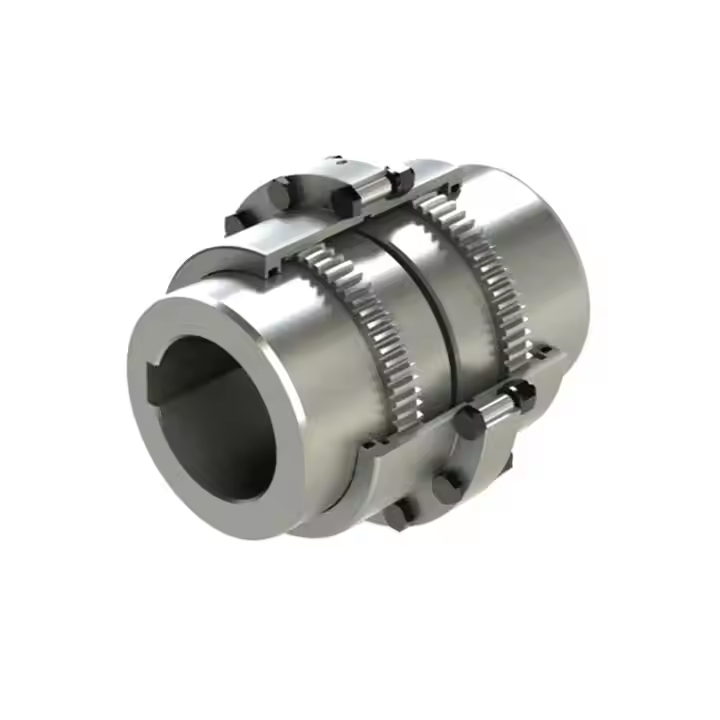


The Basic Function of a Coupling
The primary function of a Coupling is to transfer rotational motion between two shafts while maintaining mechanical continuity. This allows motors, gearboxes, pumps, and other components to operate as a unified system.
In real-world applications, perfect shaft alignment is rare. A properly designed Coupling compensates for small angular, parallel, or axial misalignments, helping reduce wear on bearings and shafts. This capability makes Coupling components indispensable in continuous-operation environments.
How a Coupling Works in Mechanical Systems
A Coupling works by mechanically linking two shafts so that torque generated by a driving component can be transmitted to a driven component. Depending on the design, the Coupling may use rigid elements, flexible elements, or a combination of both.
During operation, the Coupling absorbs minor movement and vibration between connected parts. This reduces shock loads and improves overall system stability. From a production perspective, maintaining dimensional accuracy during manufacturing is critical to ensure consistent Coupling performance across different applications.
Main Components of a Coupling
Although designs vary, most Coupling products consist of several common elements:
·Connection hubs that attach to shafts
·Transmission elements that carry torque
·Flexible or compensating structures (if applicable)
·Fastening or locking mechanisms
Each component must be produced with controlled tolerances to ensure proper fit and long-term reliability. Manufacturer-level production processes help ensure consistency, especially for large-volume supply.
Types of Coupling Designs
Coupling designs can be broadly categorized based on their structural and functional characteristics. Some are designed to be rigid, while others allow flexibility to accommodate misalignment or vibration.
Regardless of the design approach, the goal remains the same: reliable torque transmission with minimal energy loss. Standardized production methods help ensure that each Coupling performs as expected under similar operating conditions.
Why Coupling Quality Matters
The performance of a Coupling has a direct impact on the reliability of the entire mechanical system. Poor-quality Coupling components can lead to increased vibration, accelerated wear, and unexpected equipment downtime.
This is why many industrial users prioritize Couplings produced through controlled manufacturing processes, where material selection, machining accuracy, and inspection procedures are carefully managed.
Coupling Applications Across Industries
Coupling solutions are used in a wide range of industries, including:
·Manufacturing and processing equipment
·Power generation systems
·Mining and heavy machinery
·Material handling and conveyor systems
In these sectors, the ability to provide stable bulk supply from a reliable production source is often a key requirement for long-term projects and maintenance planning.
Manufacturing and Production Considerations
From a manufacturing standpoint, producing a high-quality Coupling requires attention to material properties, heat treatment, machining precision, and surface finishing. Consistent production processes ensure that each Coupling meets performance expectations.
For industrial buyers, working with a manufacturer capable of supporting scalable production and bulk supply helps reduce procurement risks and ensures continuity across equipment installations.
Installation and Maintenance Basics
Proper installation plays an important role in Coupling performance. Shafts should be aligned within acceptable tolerances, and fastening elements should be secured according to recommended guidelines.
Routine inspection and maintenance help identify early signs of wear or misalignment. Addressing these issues promptly can significantly extend the service life of the Coupling and the connected equipment.
Final Thoughts on Coupling
A Coupling is a fundamental mechanical component that enables reliable power transmission, protects connected equipment, and improves overall system performance. Its role in accommodating misalignment and reducing mechanical stress makes it essential across a wide range of industrial applications.
As demand for reliable machinery continues to grow, the importance of standardized Coupling production, manufacturer-level quality control, and dependable bulk supply will remain central to meeting industrial needs.
References
GB/T 7714:Collins J A, Busby H R, Staab G H. Mechanical design of machine elements and machines: a failure prevention perspective[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2009.
MLA:Collins, Jack A., Henry R. Busby, and George H. Staab. Mechanical design of machine elements and machines: a failure prevention perspective. John Wiley & Sons, 2009.
APA:Collins, J. A., Busby, H. R., & Staab, G. H. (2009). Mechanical design of machine elements and machines: a failure prevention perspective. John Wiley & Sons.